Public-Private Partnerships Power of PPP Toolkits

Definition of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are collaborative agreements between government entities and private sector organizations to jointly deliver public projects or services, combining resources, expertise, and risk-sharing to achieve common goals.
Importance of PPPs in Infrastructure Development
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) play a crucial role in infrastructure development by leveraging the strengths of both the public and private sectors.
Access to Capital
PPPs enable governments to access additional sources of capital from private investors, reducing the burden on public finances.
Funding Access
Accessing funding for infrastructure projects requires careful planning, project preparation, and collaboration between governments, financiers, and other stakeholders.
Risk Sharing
Effective risk sharing in PPPs encourages collaboration and incentivizes each party to leverage its strengths. This collaborative approach enhances project resilience and can lead to better outcomes for both partners and the community they serve.
Innovation
Innovation plays a crucial role in Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs), driving efficiency, effectiveness, and long-term sustainability. By harnessing the expertise and resources of both the public and private sectors, PPPs can foster innovation across various domains, including technology, financing, and service delivery.
Timely Delivery
Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Toolkit as a resource is designed to address one of the critical challenges in PPP projects i.e. timely delivery. It ensures projects are completed within specified timeframes. Timely delivery of PPP projects is essential for maximizing the benefits of PPPs, minimizing costs, and meeting public service demands efficiently.
Economic Development
The Economic Development in Public-Private Partnership (PPP) toolkit serves as a comprehensive guide for leveraging PPPs to stimulate economic growth and development. This toolkit encompasses various strategies and best practices aimed at fostering collaboration between the public and private sectors to achieve sustainable economic outcomes.
Purpose of PPP Toolkits
The purpose of Public-Private Partnership (PPP) toolkits is to provide comprehensive guidance and resources to governments, policymakers, and practitioners involved in developing, implementing, and managing PPP projects.
Guidance
PPP Toolkits offer step-by-step guidance on project identification, structuring, and implementation, assisting governments in navigating complex processes.
Capacity Building
Toolkits help build the capacity of government officials and stakeholders. It does so by providing training materials, case studies, and best practices in PPP development and management.
Standardization
PPP toolkits promote the standardization of PPP practices and procedures across different jurisdictions.
Stakeholder Engagement
Stakeholder engagement is a critical process involving individuals, groups, or organizations with a vested interest. Stakeholder engagement is essential for ensuring that projects, policies, and decisions reflect the diverse perspectives, interests, and concerns of all relevant stakeholders.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Legal and regulatory frameworks provide the structure and guidelines for governing various aspects of society, including business activities, public administration, and individual rights.
Knowledge Sharing
They serve as platforms for knowledge sharing and peer learning, enabling governments to exchange experiences, lessons learned, and emerging trends in PPP development.
Types of PPP Models
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) encompass various models and structures that facilitate collaboration between the public and private sectors in delivering infrastructure projects and public services.
Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT)
Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) is where a private sector entity is responsible for financing, designing, constructing, and operating a public infrastructure project for a specified period. BOT arrangements are commonly used for large-scale infrastructure projects such as toll roads, bridges, ports, and power plants.

One prominent example of a Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) project in India is the Delhi-Gurgaon Expressway. The Delhi-Gurgaon Expressway project aimed to address the growing traffic congestion and improve transportation infrastructure in the National Capital Region (NCR).
The project serves as an example of how BOT projects can be used to leverage private sector expertise and investment to develop critical infrastructure and enhance connectivity in India.
Build-Own-Operate-Transfer (BOOT)
Build-Own-Operate-Transfer (BOOT) is where a private sector entity finances, constructs, owns, and operates a public infrastructure project for a specified period, typically under a concession agreement. BOOT arrangements are often used for projects such as water treatment plants, airports, and telecommunications networks.
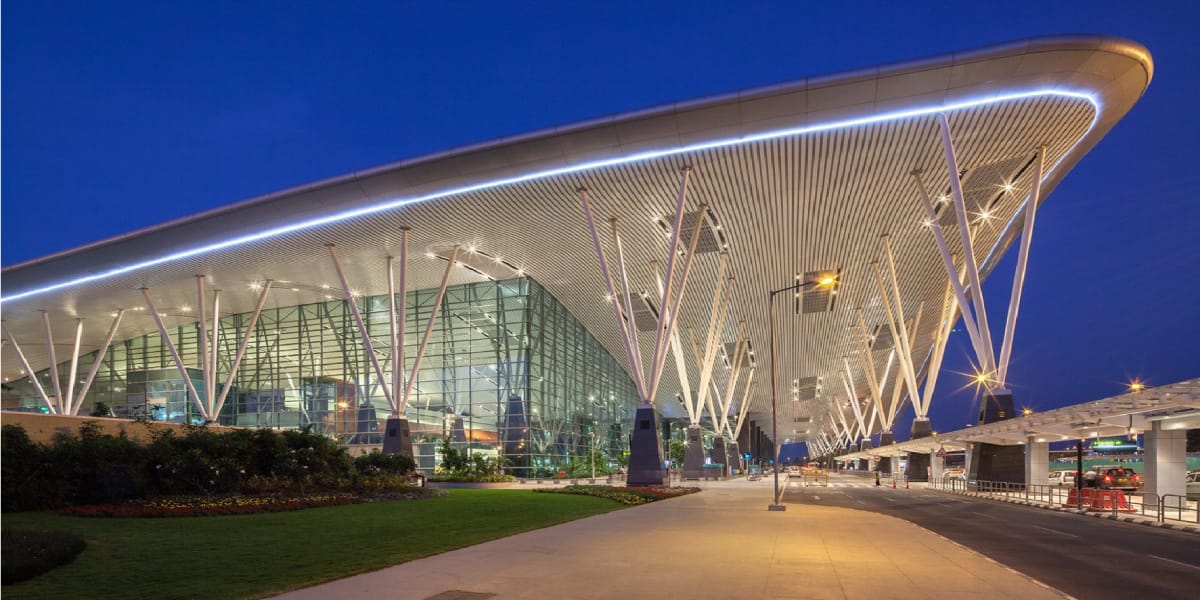

One notable example of a Build-Own-Operate-Transfer (BOOT) project in India is the Bengaluru International Airport. The Bengaluru International Airport project aimed to address the increasing air traffic demand in Bengaluru and provide world-class infrastructure and services to passengers and airlines.
The airport has since become one of the busiest airports in India, serving as a major gateway for domestic and international air travel and contributing to the economic growth and development of the region. The success of the Bengaluru International Airport project showcases how BOOT projects can leverage private sector expertise and investment to develop critical infrastructure and enhance connectivity in India.
Design-Build-Finance-Operate (DBFO)
Design-Build-Finance-Operate (DBFO) is where a private entity is responsible for designing, building, financing, and operating a public infrastructure project. In DBFO arrangements, the private sector entity often takes on additional responsibilities such as maintenance and facility management during the operational phase.
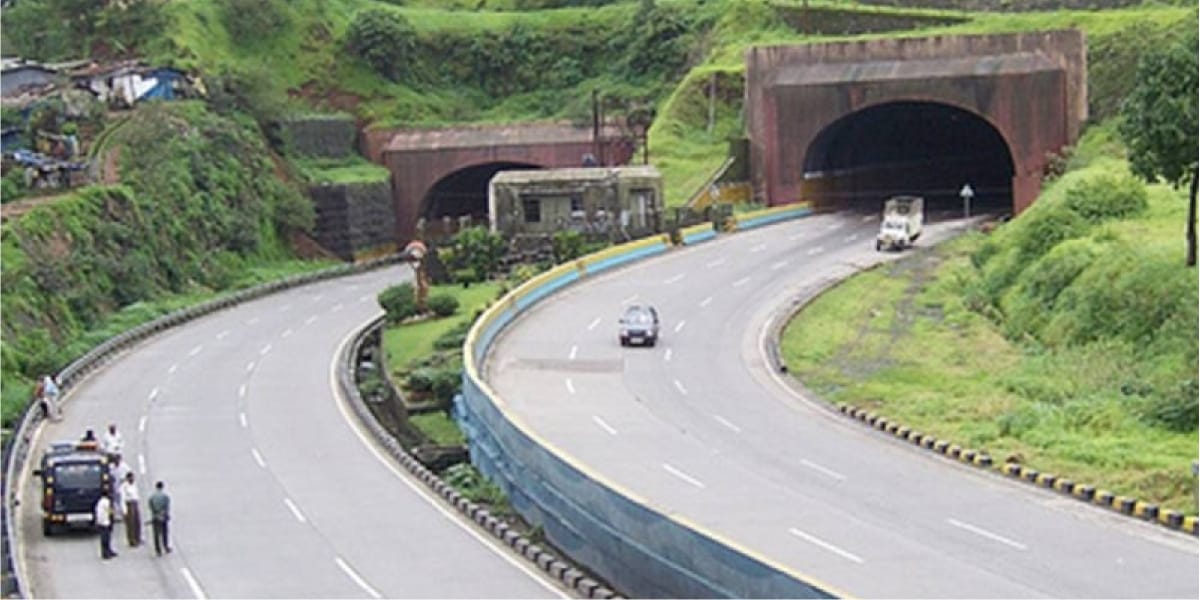

One notable example of a Design-Build-Finance-Operate (DBFO) project in India is the Mumbai-Pune Expressway. The Mumbai-Pune Expressway project aimed to alleviate traffic congestion on the existing Mumbai-Pune highway and improve connectivity between the two cities.
The success of the Mumbai-Pune Expressway project demonstrates how DBFO projects can leverage private sector expertise and financing to deliver critical infrastructure and address transportation challenges in India.
By partnering with the private sector, government agencies can accelerate the development of infrastructure projects and achieve better value for money while transferring operational risks to the private sector.
Key Components of Successful PPPs
Successful Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) rely on several key components to ensure effective collaboration, efficient project delivery, and sustainable outcomes.
Clear Objectives and Scope
Clear objectives and scope are foundational to successful Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs). They involve defining the project's purpose, goals, and desired outcomes, as well as outlining the specific services or infrastructure to be provided.
Risk Allocation
Risk allocation refers to the process of assigning various types of risks associated with a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) to the party best equipped to manage or mitigate them. This involves identifying, assessing, and allocating risks related to financial, technical, operational, legal, and political aspects of the project.
Legal and Regulatory Framework
The legal and regulatory framework forms the backbone of any successful Public-Private Partnership (PPP). It comprises laws, regulations, policies, and contractual agreements that govern the rights, responsibilities, and obligations of the parties involved in the PPP process.
Financial Viability
Financial viability is critical for the success of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs), ensuring that projects are economically feasible and sustainable over their lifecycle. It involves assessing the project's ability to generate sufficient revenue to cover costs, including initial investment.
Project Assessment and Feasibility Studies
Project assessment and feasibility studies are crucial preliminary steps in the development of Public-Private Partnership (PPP) projects. These studies involve comprehensive evaluations of technical, financial, economic, legal, and environmental.
Framework Establishment
Develop a comprehensive legal and regulatory framework that provides clarity, consistency, and transparency for PPP projects.
Procurement Laws
Ensure that procurement laws and regulations are in place to govern the selection process for private sector partners, promoting fairness, competition, and transparency.
Concession Agreements
Draft clear and enforceable concession agreements that outline the rights, responsibilities, and obligations of each party involved in the PPP, including risk allocation, performance standards, and dispute resolution mechanisms.

Financial Structuring and Risk Management
Financial Structuring
Capital Stack Develop a well-balanced capital structure that combines various sources of financing, including equity, debt, grants, and subsidies, to optimize funding and minimize financing costs.
Debt Financing Identify appropriate debt instruments, such as bank loans, bonds, or project finance, to raise funds for PPP projects while considering debt service coverage ratios, interest rates, and repayment terms.
Equity Financing Secure equity contributions from private sector investors or consortium partners to finance project development and mitigate financial risks, ensuring alignment of interests and incentives.
Revenue Streams Determine reliable and sustainable revenue streams, such as user fees, availability payments, or government subsidies, to support project financing and ensure the financial viability of PPP projects.
Financial Models Develop robust financial models to assess project cash flows, evaluate investment returns, and conduct sensitivity analysis to identify potential risks and mitigate financial uncertainties.
Risk Management
Risk Identification: To develop risk mitigation strategies and identify and assess potential risks associated with PPP projects, including financial, technical, operational, legal, environmental, and political risks.
Risk Allocation Allocate risks between the public and private sectors through contractual agreements, insurance mechanisms, and risk-sharing arrangements to ensure that risks are borne by the party best equipped to manage them.
Insurance and Guarantees Obtain insurance policies, guarantees, or other risk mitigation instruments to protect against unexpected events that may impact project performance, such as construction delays, revenue shortfalls, or force majeure events.
Contingency Planning Develop contingency plans and risk mitigation measures to address potential project disruptions or deviations from the original plan, ensuring that projects remain on track and within budget.
Leveraging PPP Toolkits for Effective Project Implementation
Leveraging PPP toolkits for effective project implementation involves utilizing the comprehensive resources provided to streamline planning, execution, and management.
These toolkits offer guidance, templates, and best practices tailored to PPP projects, helping stakeholders navigate complex processes, mitigate risks, and ensure success.
Pre-Implementation Phase
The pre-implementation phase of a PPP project involves preparatory activities such as project identification, feasibility studies, stakeholder engagement, legal and regulatory framework development, financial structuring, procurement planning, risk assessment, and capacity building.
Structuring and Funding Mechanisms
Structuring involves designing the financial framework of a project or transaction to optimize its capital structure, risk profile, and cash flows. It encompasses various techniques like debt/equity mix, interest rate management, and asset/liability matching to achieve desired financial objectives.
Stakeholder Engagement and Communication
Stakeholder engagement and communication are critical components of successful project management and organizational effectiveness. Stakeholder engagement involves identifying and involving individuals or groups affected by or interested in the project or organization.
Implementation Phase
The implementation phase of a PPP project is the stage where the planned activities are executed to bring the project to fruition. This phase involves the physical construction, development, and operation of the infrastructure or service as outlined in the project plan and contractual agreements
Post-implementation phase
Monitoring Performance
Continuously monitoring the performance of the implemented solution to ensure it meets the desired objectives and delivers expected outcomes.
Evaluation
Assessing the effectiveness and efficiency of the implemented solution against predefined success criteria. This may involve collecting feedback from stakeholders, conducting reviews, and analyzing performance metrics.
Issue Resolution
Addressing any issues, challenges, or deficiencies identified during monitoring and evaluation. This may require making adjustments, improvements, or corrections to the implemented solution.
Optimization
Identifying opportunities for optimization and enhancement to improve the performance, functionality, or usability of the implemented solution.
Training and Support
Providing ongoing training and support to users and stakeholders to ensure they can effectively utilize and maintain the implemented solution.
Conclusion
PPP toolkits are indispensable resources for governments and stakeholders involved in infrastructure development. They streamline project processes, promote transparency, and mitigate risks, leading to more efficient and successful outcomes.
As countries worldwide seek to address infrastructure gaps, strategically using PPP toolkits remains crucial for maximizing value and delivering sustainable solutions.
